Erciyes Mount
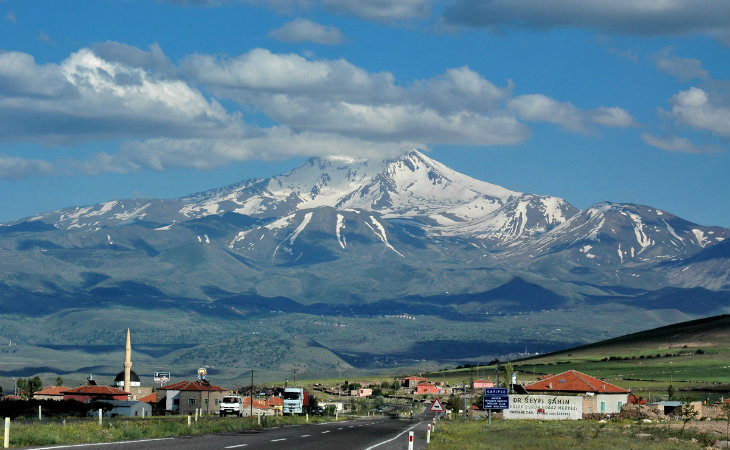
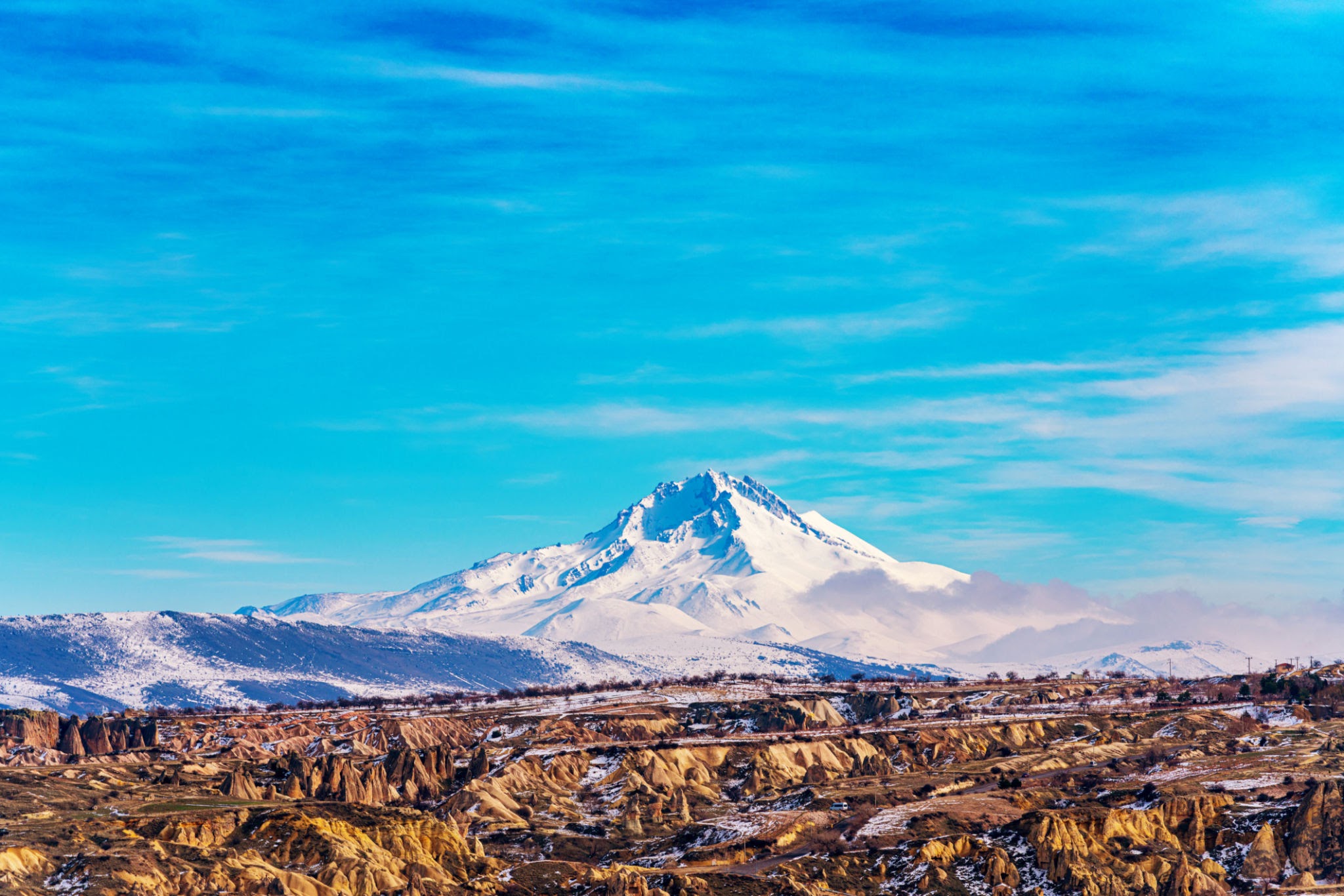
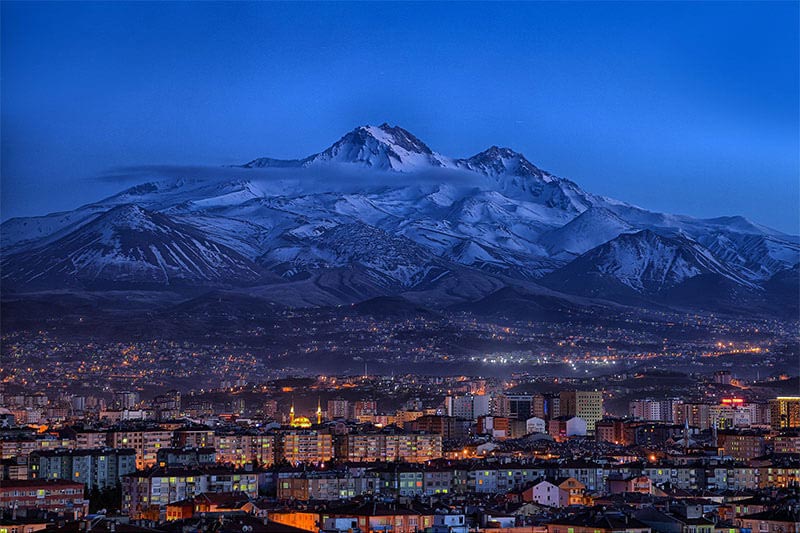
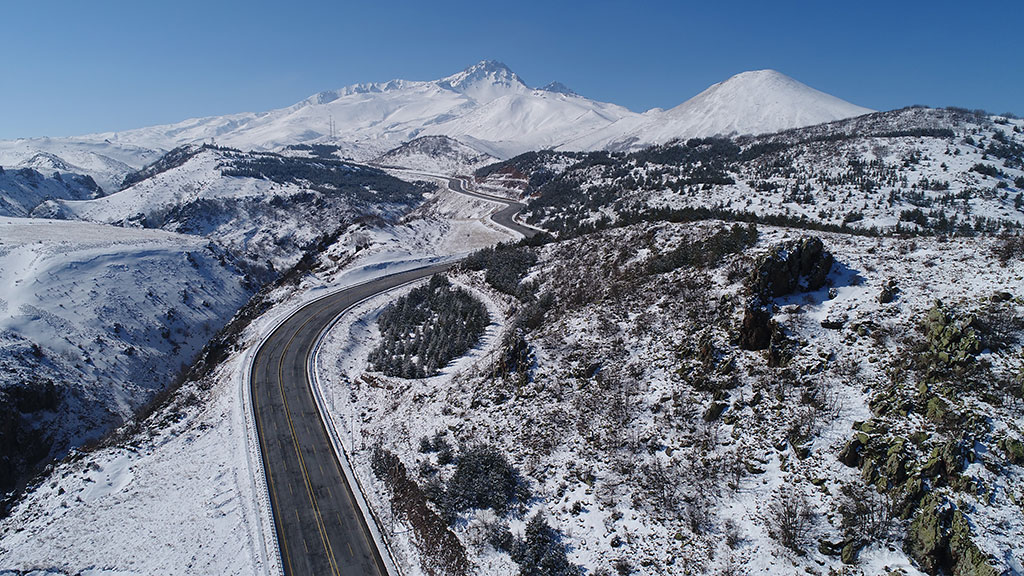
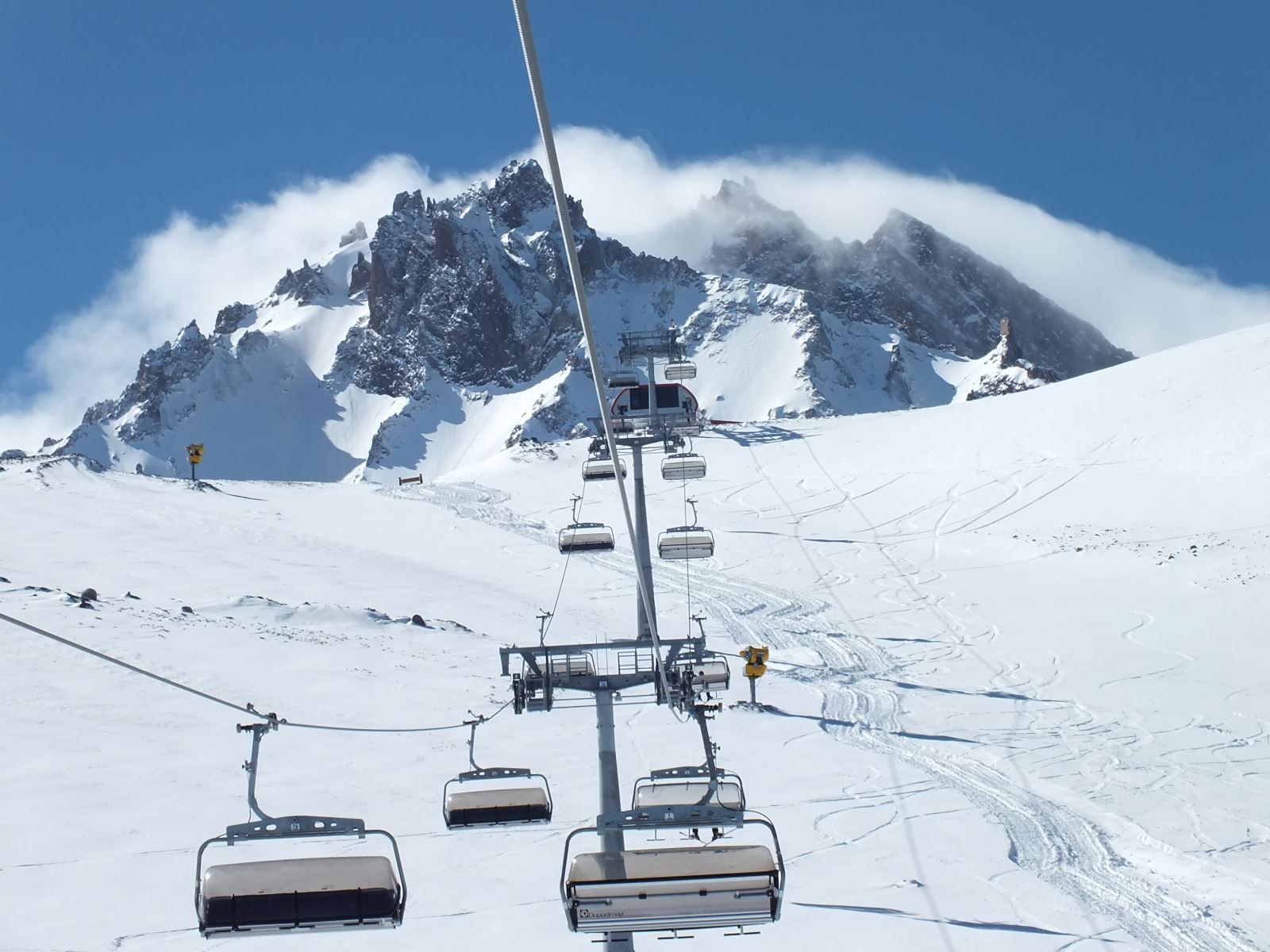
Erciyes Mountain is an extinct volcano located in the Central Anatolia Region. Sultansazlığı, 25 km southwest of Kayseri, is a massive stratovolcano rising from the plains. The highly eroded volcano can be said to have last erupted in 253 BC, based on the depictions on Roman coins. Erciyes is the highest mountain in Central Anatolia with its peak reaching 3,917 meters. It covers an area of 3300 square kilometers. It is considered to be the highest point of the Aladağlar, the northeastern extension of the Taurus Mountains, and is included in the Alpine belt. The mountain got its Turkish name from the Ancient Greek word Argaeus (Ἀργαῖος). The famous traveler and geographer Strabo wrote in his Geographika that its summit was never cleared of snow and that the Black Sea and the Mediterranean could be seen from its summit on a clear day. Today, it is not possible to see the Mediterranean and the Black Sea from the summit of Erciyes, which only has a glacier on the northern slope of its summit, due to the roundness of the Earth.